Introduction: The Future of Autonomy in Driving and Robotics
The dawn of autonomous systems is transforming industries across the globe, with significant advancements in fields like autonomous driving and robotics. These systems—ranging from self-driving cars to intelligent robots—are continuously evolving, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cutting-edge sensor technologies. The goal is simple but ambitious: to create machines that can perceive the world as humans do, make intelligent decisions, and act autonomously, enhancing the quality of life, safety, and productivity.
Autonomous driving, which aims to create self-driving vehicles that operate without human intervention, has seen significant strides in recent years. Likewise, robotics, which has traditionally involved machines performing repetitive tasks under human control, is now evolving toward robots that can perceive, understand, and make decisions in dynamic environments. Both industries are developing critical systems for perception and decision-making, crucial components that enable autonomous operations.
This article delves into the ongoing advancements in autonomous perception and intelligent decision-making within these two fields. We will explore the technologies behind them, the challenges they face, and the future possibilities that lie ahead for autonomous driving and robotics.
1. The Evolution of Autonomous Driving: Perception and Decision-Making
1.1 What is Autonomous Driving?
Autonomous driving refers to the development of self-driving vehicles that can navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make driving decisions without human input. These vehicles use a combination of sensors, AI, and machine learning algorithms to interpret their environment and make real-time decisions.
The key technology enabling autonomous vehicles includes:
- LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LIDAR sensors emit laser beams to scan the environment and create detailed 3D maps of the surroundings, allowing the vehicle to perceive obstacles, traffic signals, and road conditions.
- Cameras: High-definition cameras are used for object recognition, such as detecting pedestrians, other vehicles, road signs, and lane markings.
- Radar: Radar sensors can measure the speed and distance of objects, providing an additional layer of perception, especially in low visibility conditions like fog or rain.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors help in detecting nearby objects at close range, such as when parking.
1.2 The Role of AI in Autonomous Driving Perception
AI plays a critical role in enabling autonomous vehicles to process the vast amounts of data collected by these sensors. Through machine learning techniques, AI systems can recognize and classify objects, track moving elements, and predict the future behavior of vehicles, pedestrians, or other obstacles.
One of the primary challenges in autonomous driving is ensuring the vehicle can “understand” its environment accurately. This involves detecting and interpreting multiple inputs in real-time, which requires a high level of computational power. AI systems are trained on vast datasets of driving scenarios, enabling them to recognize patterns and make sense of complex road situations.
- Object Detection and Classification: Machine learning algorithms enable vehicles to detect objects, such as other cars, pedestrians, cyclists, and animals, and classify them in real-time. This is essential for decision-making in dynamic environments.
- Path Planning: AI is responsible for deciding the best route to take, avoiding obstacles, and choosing when to speed up, slow down, or change lanes.
Real-World Example:
Tesla’s Autopilot system is one of the most advanced autonomous driving systems currently available. Using a combination of cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and AI algorithms, Tesla vehicles can navigate highways, change lanes, and park autonomously. However, full autonomy remains a work in progress, with continuous updates being made to improve the system’s accuracy and safety.
1.3 Decision-Making in Autonomous Driving
In addition to perception, intelligent decision-making is at the core of autonomous driving. The system must evaluate the data provided by sensors and make real-time decisions regarding the vehicle’s actions. This includes decisions on:
- Speed Control: The system must decide when to accelerate or decelerate based on road conditions, traffic flow, and proximity to other vehicles.
- Traffic Signal Recognition: Recognizing and responding to traffic lights and stop signs is a fundamental decision for autonomous vehicles.
- Obstacle Avoidance: The AI system must quickly calculate the best maneuver to avoid pedestrians, other cars, or roadblocks, while ensuring safety.
The decision-making process often involves ethical considerations, such as how to respond in a situation where an accident may be unavoidable (e.g., a choice between hitting a pedestrian or swerving into a guardrail). These ethical dilemmas are the subject of much debate, and different approaches to programming autonomous vehicles’ decision-making have been proposed.
2. The Advancements in Robotics: Autonomous Perception and Intelligent Decision-Making
2.1 The Role of AI in Robotics
Robotics has long been a staple in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. However, traditional robots operated under strict pre-defined rules and needed human oversight. The real innovation in modern robotics lies in the integration of AI that enables robots to perceive and understand their environment, make decisions, and learn from their experiences.
The use of AI in robotics enables machines to autonomously perform complex tasks, such as navigating dynamic environments, interacting with humans, and learning new tasks without direct human intervention.
2.2 Autonomous Perception in Robotics
Robots equipped with AI can perceive their environment through sensors like LIDAR, cameras, and depth sensors. However, it’s not just about collecting data; it’s about interpreting and understanding that data in a meaningful way.
- Visual Perception: Robots use cameras and computer vision algorithms to recognize objects, people, and obstacles in their environment. This is particularly useful in applications like autonomous delivery or surgery, where the robot needs to understand complex scenes.
- Spatial Awareness: LIDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors allow robots to understand the distance between objects, providing a sense of “depth” to their surroundings. This helps them navigate spaces and avoid obstacles effectively.
- Sensor Fusion: Modern robots use a combination of different sensor types to get a more complete understanding of their environment. By fusing data from multiple sensors, robots can make more accurate decisions, even in challenging conditions.
2.3 Intelligent Decision-Making in Robotics
Robots must decide how to act based on the data they receive from their sensors. This involves evaluating multiple factors, such as the urgency of a task, safety considerations, and resource availability.
- Path Planning: Similar to autonomous vehicles, robots need algorithms that allow them to navigate a space efficiently. Whether it’s a warehouse robot picking up an item or a drone delivering a package, the robot must plan its route while avoiding obstacles.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Many modern robots are designed to interact with humans. They must make decisions about when to approach, how to communicate, and how to react to human gestures or voice commands.
- Learning and Adaptation: AI-powered robots can improve their performance over time through reinforcement learning. For example, a robot used in manufacturing can adjust its operations based on feedback from the environment or from its own experiences, thereby optimizing its actions for greater efficiency.
Real-World Example:
Boston Dynamics’ Spot robot is an excellent example of advanced robotic perception and decision-making. Spot uses AI and a combination of sensors to navigate various environments, perform inspections, and even interact with people. Its ability to maintain balance, avoid obstacles, and work in dynamic settings demonstrates the power of intelligent decision-making in robotics.
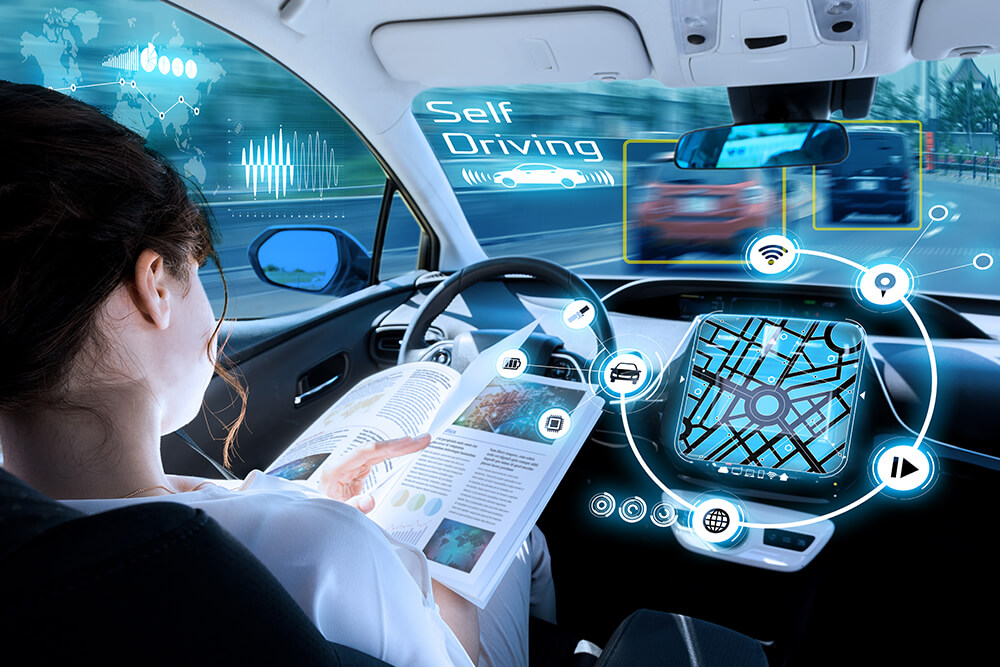

3. Challenges in Autonomous Systems: Addressing Perception and Decision-Making Limitations
While autonomous driving and robotics have seen impressive advancements, they still face significant challenges. Ensuring that these systems can operate safely and efficiently in dynamic and unpredictable environments is crucial.
3.1 Perception Challenges
- Complex Environments: Autonomous systems must function in environments filled with dynamic, unpredictable elements such as pedestrians, animals, weather conditions, and other vehicles. Processing data from a variety of sensors in real-time to create a clear, accurate picture of the environment is a major challenge.
- Sensor Limitations: While LIDAR, radar, and cameras are powerful tools, they still have limitations. For instance, LIDAR may struggle in heavy rain or snow, while cameras may be unable to see in low light conditions.
- Data Overload: Autonomous systems must process a massive amount of data from multiple sensors simultaneously. The challenge is ensuring that the AI system can prioritize the most relevant data for quick decision-making.
3.2 Decision-Making Challenges
- Ethical Dilemmas: One of the biggest challenges in autonomous decision-making, particularly for self-driving cars, is addressing ethical dilemmas. What should a vehicle do when faced with an unavoidable accident? Designing a system that can handle these decisions ethically remains an ongoing challenge.
- Uncertainty and Risk: Autonomous systems often need to make decisions in uncertain environments. For example, a robot in a warehouse might need to choose whether to move toward a stack of boxes or wait for another robot to clear the path. Balancing risk and ensuring safe decisions is key.
4. The Future of Autonomous Driving and Robotics
4.1 Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
As AI continues to evolve, both autonomous driving and robotics are poised for even greater breakthroughs. AI systems will become more advanced in recognizing patterns, predicting outcomes, and learning from real-world experiences. In autonomous driving, this could mean safer, more reliable vehicles with the ability to adapt to any situation. In robotics, this could lead to machines capable of performing even more complex tasks and learning from their environment.
4.2 Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
As autonomous systems become more integrated into society, addressing ethical and regulatory concerns will be crucial. Governments and industry leaders will need to collaborate to establish frameworks that ensure these systems operate safely and ethically.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Autonomy
The advancements in autonomous driving and robotics are reshaping industries and societies across the globe. With the continuous evolution of AI, these systems are becoming more intelligent, capable, and reliable. While challenges remain, the future holds great promise for self-driving cars and robots that can autonomously perceive and make decisions. As these technologies continue to mature, we can expect a world where autonomy enhances productivity, safety, and convenience, ultimately improving the way we live and work.