Introduction
In recent years, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in public safety has emerged as a critical tool for crime prevention, monitoring, and law enforcement. AI-powered systems, including smart surveillance, predictive analytics, and data-driven decision-making, are reshaping the landscape of law enforcement by enhancing both preventive and reactive measures. Through AI, cities, law enforcement agencies, and security systems are now equipped with cutting-edge technologies that can help reduce crime rates and enhance community safety.
From smart surveillance systems equipped with facial recognition capabilities to AI-driven predictive crime analytics, the integration of AI is not only helping to solve crimes faster but also allowing for proactive strategies to prevent them before they happen. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI tools identify patterns, predict where crimes are likely to occur, and optimize responses, making cities safer and more secure.
This article explores how AI is being applied in the field of public safety, with a particular focus on its use in intelligent surveillance and predictive analytics to reduce crime rates. We will examine various case studies of AI implementations, the technologies behind them, the benefits, challenges, and ethical considerations associated with these advancements, and the future of AI in public safety.
Section 1: Overview of AI in Public Safety
1.1. The Role of AI in Law Enforcement
Artificial intelligence in public safety spans several domains, including crime prediction, law enforcement operations, emergency response, and crime analysis. At its core, AI helps law enforcement agencies make faster, data-informed decisions, automate routine tasks, and identify trends that human officers may overlook.
1.1.1. Crime Prediction and Prevention
AI-powered systems use historical crime data and other contextual information (e.g., location, time, weather, and social patterns) to predict where crimes are likely to occur. This helps law enforcement allocate resources more effectively, placing officers in high-risk areas at times when crimes are most likely to happen. Predictive policing, a form of crime forecasting, is a prime example of this application.
1.1.2. Smart Surveillance Systems
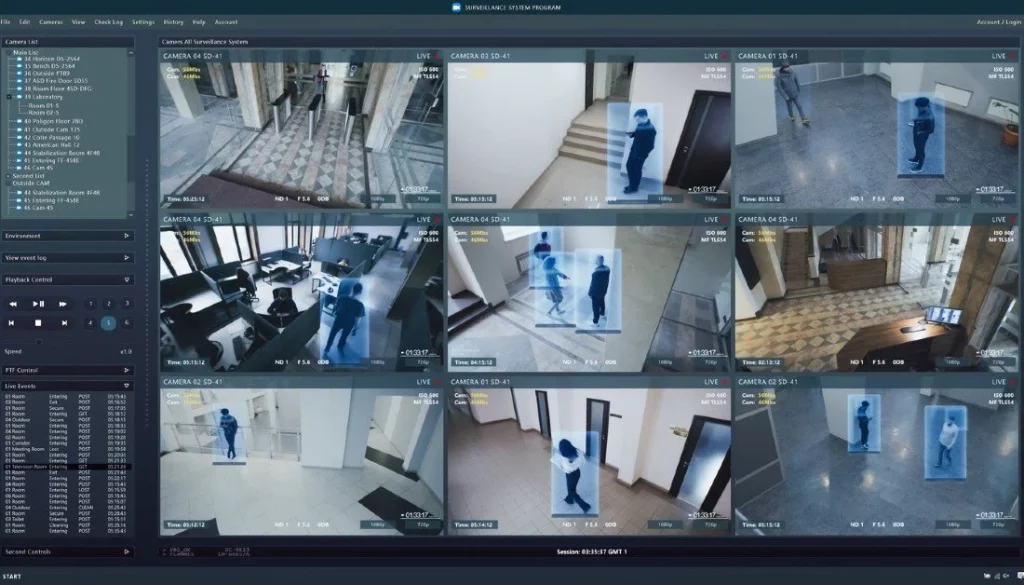
AI-enhanced surveillance systems are transforming how cities monitor public spaces. These systems can identify suspicious behavior, recognize faces in crowded places, and detect potential threats in real-time. This type of surveillance often works alongside facial recognition technology, helping law enforcement identify individuals in a crowd or track criminals in real-time.
Section 2: AI-Powered Smart Surveillance in Public Safety
2.1. The Technology Behind Smart Surveillance
Smart surveillance systems use advanced AI algorithms to analyze data from video cameras and other sensors. These systems can detect unusual behaviors, such as people loitering in a high-risk area, unattended bags, or vehicles parked in restricted zones. The technology behind these systems involves machine learning (ML) algorithms, computer vision, and facial recognition.
2.1.1. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Computer vision algorithms allow surveillance systems to “see” and interpret video footage the same way the human brain processes visual information. This capability makes it possible for AI systems to identify patterns in human behavior and detect any anomalies that could signal a crime or threat. For instance, if a person is seen acting suspiciously, the system can alert security personnel, who can then investigate further.
2.1.2. Facial Recognition and Identity Verification
Facial recognition is one of the most controversial yet effective AI tools in public safety. AI systems can scan faces captured in video footage and compare them against databases of known criminals or missing persons. This technology is already being used in various public spaces, including airports, shopping malls, and city streets, to identify individuals who may pose a threat.
One notable example is the use of facial recognition at large public events or protests, where AI can detect individuals with outstanding warrants or previous criminal records.
2.2. Real-World Case Studies of Smart Surveillance
2.2.1. London’s Public Surveillance Network
London has one of the largest public surveillance networks in the world, with thousands of cameras equipped with AI-based video analytics. The city’s surveillance system uses AI to monitor areas for unusual activity, such as aggressive behavior or unattended bags. In 2019, London’s Metropolitan Police introduced AI software to help identify “hot spots” of criminal activity. This software uses data from CCTV footage to predict where crimes are likely to occur, allowing police to respond faster and more effectively.
2.2.2. New York City’s Predictive Policing with AI-Enhanced Cameras
New York City’s public safety efforts also incorporate AI surveillance. The city uses AI-powered cameras with object detection capabilities to monitor crime-prone areas. The AI system automatically alerts law enforcement when suspicious activity, such as violent altercations, occurs. The system has helped reduce incidents of violent crimes in several neighborhoods.
Section 3: Predictive Analytics in Crime Prevention
3.1. What Is Predictive Policing?
Predictive policing involves using AI to analyze historical crime data and identify patterns that suggest where future crimes are likely to occur. By identifying “hot spots” for criminal activity, law enforcement can deploy officers to high-risk areas before crimes happen. Predictive analytics is based on data-driven algorithms that analyze various variables, including time of day, location, weather, and community events.
3.1.1. Key Technologies in Predictive Policing
Machine learning algorithms are the backbone of predictive policing. These algorithms analyze data from past crimes, including location, time, and method of crime, to predict where similar crimes are likely to occur. Some systems even integrate social media and other open-source data to refine their predictions.
3.1.2. Benefits of Predictive Policing
Predictive policing offers several benefits, including:
- Efficient Allocation of Resources: By predicting crime hotspots, police departments can allocate officers to the areas most likely to experience criminal activity, improving both the effectiveness and efficiency of law enforcement.
- Crime Deterrence: The presence of police officers in high-risk areas, due to predictive analytics, can deter potential offenders from committing crimes in the first place.
- Improved Response Times: By predicting when and where crimes are likely to occur, police departments can ensure faster response times and potentially prevent crimes from escalating.
Section 4: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
4.1. Concerns Over Privacy and Civil Liberties
AI-powered surveillance and predictive policing have raised significant concerns regarding privacy and civil liberties. For example, facial recognition technologies have sparked debates over whether individuals are being unfairly tracked or monitored without their consent.
Some critics argue that AI tools could lead to racial profiling or unfair targeting of certain groups, particularly in communities already affected by over-policing. Others worry about the potential misuse of AI surveillance data for non-law enforcement purposes.
4.1.1. Ethical Use of AI in Public Safety
As AI technology becomes more prevalent, it is critical that law enforcement agencies adopt ethical frameworks to ensure the responsible use of AI tools. This includes transparency in the use of AI surveillance, as well as protections for citizens’ privacy and rights. Additionally, AI systems should be regularly audited to ensure they are functioning as intended and not disproportionately affecting certain demographics.
4.2. Accuracy and Bias in AI Algorithms
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the data is biased or incomplete, the AI system’s predictions and decisions can be skewed, leading to inaccurate or discriminatory outcomes. For example, predictive policing algorithms may perpetuate historical biases if they rely on data from areas that have historically been over-policed or have higher rates of arrests for minor offenses.
4.2.1. Addressing Bias in AI Algorithms
It is essential to regularly audit AI systems to ensure they are free from biases and that the data used to train them is representative of the community as a whole. Additionally, AI algorithms should be transparent and allow for human oversight, especially when it comes to making critical law enforcement decisions.
Section 5: The Future of AI in Public Safety
5.1. The Integration of AI with Other Technologies
In the future, AI is likely to become even more integrated with other technologies to enhance public safety. For instance, AI could work alongside drones, robots, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create more dynamic and effective public safety systems. These systems could include real-time data from wearable devices, environmental sensors, and traffic monitoring systems.
5.2. Potential for Global Adoption
As AI technology improves and becomes more affordable, there is potential for its widespread adoption by law enforcement agencies around the world. Cities that are currently hesitant to adopt AI in public safety may begin to see the value of these technologies in reducing crime rates and improving overall public security.
5.3. Innovations on the Horizon
The future of AI in public safety looks promising, with ongoing advancements in natural language processing (NLP) for better crime reporting, AI-driven analysis of body cam footage, and even AI systems capable of preventing cybercrime. Additionally, AI could become a key tool in crisis management, helping emergency responders assess situations and respond more effectively.
Conclusion
AI is fundamentally changing how we approach public safety. By enhancing surveillance systems, predicting criminal activity, and automating crime detection, AI is making it possible to not only respond to crime more efficiently but also to prevent it before it happens. However, as we continue to embrace these technologies, it is crucial that we address the ethical concerns surrounding privacy, bias, and accountability.
As AI in public safety continues to evolve, its ability to reduce crime rates and enhance the safety of our communities will only grow. With careful oversight and ethical implementation, AI has the potential to transform public safety efforts and provide a more secure, just, and efficient society.











































