Introduction
The development of autonomous driving technology represents one of the most exciting and transformative advancements in the automotive industry. At the core of this transformation lies Artificial Intelligence (AI), which plays a critical role in enabling vehicles to operate independently without human intervention. AI technologies, including machine learning, computer vision, deep learning, and sensor fusion, are the building blocks for self-driving cars, allowing them to navigate, perceive their environment, make decisions, and learn from experience.
This article explores how AI supports the development of autonomous driving technology by examining key case studies and industry examples. It will delve into the AI techniques used in autonomous vehicles, the challenges faced in their development, and the successful implementations that are bringing us closer to the reality of fully autonomous cars.
Section 1: Overview of Autonomous Driving Technology
1.1 The Levels of Autonomous Driving
Autonomous driving technology is generally categorized into different levels based on the degree of human intervention required. These levels, defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), range from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation).
- Level 0: No automation; the driver is entirely in control.
- Level 1: Driver assistance; some automated features like adaptive cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial automation; the vehicle can control both steering and acceleration, but the driver must remain engaged.
- Level 3: Conditional automation; the vehicle can handle certain driving tasks but the driver must take control when requested.
- Level 4: High automation; the vehicle can handle all driving tasks within certain conditions, such as specific geographical areas.
- Level 5: Full automation; the vehicle can operate entirely without human intervention, under all conditions and environments.
1.2 The Role of AI in Autonomous Vehicles
AI is essential for the operation of autonomous vehicles at all levels. It enables the vehicle to:
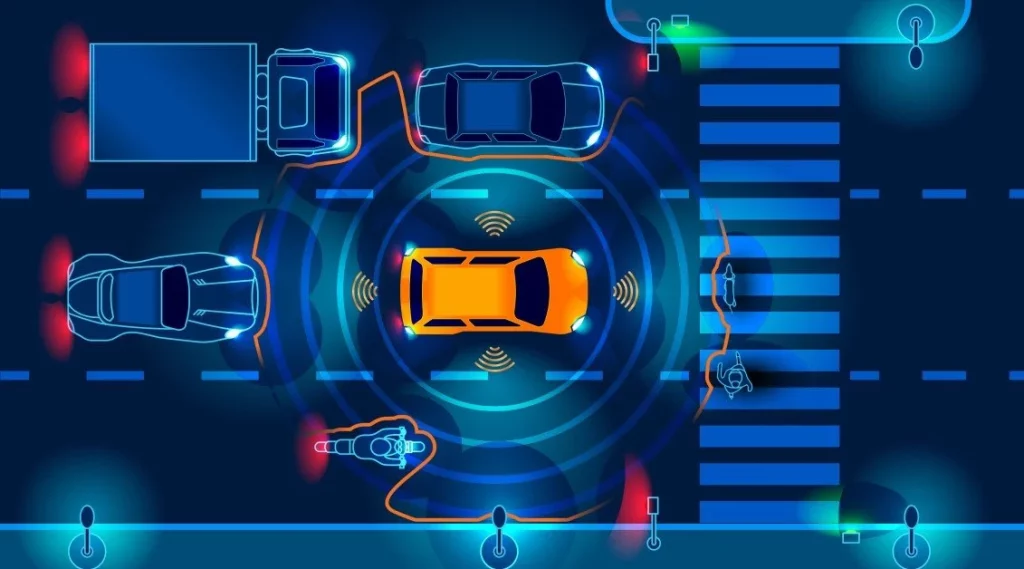
- Perceive the Environment: Using sensors like cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors, AI helps the vehicle “see” and interpret the environment in real time.
- Plan the Route: AI algorithms use map data, traffic information, and real-time data to plan and adjust the vehicle’s route.
- Make Decisions: AI models, including deep learning algorithms, make split-second decisions based on sensor data, such as when to accelerate, brake, or change lanes.
- Learn from Experience: Machine learning allows autonomous vehicles to improve their performance over time by learning from millions of miles of driving data.
Section 2: Key AI Technologies Driving Autonomous Driving
2.1 Machine Learning and Deep Learning
At the heart of autonomous driving is machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL). These AI techniques enable autonomous vehicles to recognize patterns, classify objects, and make decisions based on data.
- Object Detection and Classification: ML and DL are used for identifying objects in the vehicle’s environment, such as pedestrians, other vehicles, traffic signs, and road markings.
- Behavior Prediction: AI models predict the behavior of other drivers and pedestrians, allowing the vehicle to anticipate potential hazards and adjust its actions accordingly.
- Reinforcement Learning: This type of learning allows autonomous vehicles to improve their driving performance over time by interacting with their environment and learning from mistakes.
Case Study: Tesla’s Autopilot
Tesla’s Autopilot system is one of the leading examples of AI-driven autonomous driving. Tesla uses deep learning techniques to enable its cars to recognize and respond to their environment. The system can navigate highways, change lanes, and park autonomously in certain conditions. Tesla’s approach to autonomous driving is based on vast amounts of real-world driving data, allowing the system to learn and improve over time.
2.2 Computer Vision
Computer vision is another critical component of autonomous driving. It enables vehicles to interpret visual data from cameras and other sensors, providing the ability to “see” the world in a way similar to human perception.
- Lane Detection: Computer vision algorithms can detect lane markings on the road, allowing the vehicle to stay within its lane.
- Traffic Sign Recognition: AI uses image recognition to identify traffic signs and signals, enabling the vehicle to adhere to road rules.
- Obstacle Detection: Computer vision helps detect obstacles such as pedestrians, animals, or debris, ensuring the vehicle can navigate safely around them.
Case Study: Waymo
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet (Google’s parent company), has been a leader in autonomous driving. Its vehicles use computer vision to navigate through complex environments. Waymo cars are equipped with a variety of sensors, including LiDAR and cameras, which allow them to perceive the environment in 360 degrees. The company has been testing its autonomous vehicles in real-world scenarios for several years, and it is considered one of the pioneers in the development of self-driving technology.
2.3 Sensor Fusion
Sensor fusion refers to the process of combining data from different types of sensors, such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras, to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Enhanced Perception: Sensor fusion enables the vehicle to create a more accurate and detailed map of the environment, overcoming limitations that individual sensors may have (e.g., cameras are limited in low light, while radar has low resolution).
- Redundancy and Reliability: Multiple sensors provide redundancy, ensuring that if one sensor fails or is blocked, the vehicle can still operate safely using data from other sensors.
Case Study: Audi and Mobileye
Audi has partnered with Mobileye, an AI and computer vision company, to develop autonomous driving systems that rely on sensor fusion. Mobileye’s system uses a combination of cameras, radar, and LiDAR to provide the vehicle with a comprehensive view of its surroundings. This sensor fusion technology is critical for enabling Audi’s self-driving cars to navigate complex environments, such as city streets.
Section 3: Challenges in the Development of Autonomous Driving
3.1 Data and Training
AI models for autonomous driving require large amounts of data to train effectively. The more data an AI system receives, the better it can perform. However, obtaining high-quality data is a challenge.
- Data Collection: Collecting driving data from a wide variety of conditions (weather, traffic, road types) is essential for training robust AI systems.
- Data Labeling: Labeling data accurately is time-consuming and expensive, but it’s necessary for supervised learning algorithms to recognize objects and make correct decisions.
3.2 Safety and Testing
Ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles is paramount. AI systems must be rigorously tested to ensure they can handle any situation that might arise on the road.
- Simulation: Testing autonomous vehicles in real-world scenarios can be risky and impractical. AI systems are often trained and tested in simulation environments before they are deployed on the roads.
- Real-World Testing: Even after simulation testing, autonomous vehicles must undergo extensive real-world testing to ensure they can handle unexpected challenges, such as erratic human drivers, road conditions, and extreme weather.
3.3 Legal and Ethical Issues
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles raises legal and ethical questions:
- Liability: If an autonomous vehicle is involved in an accident, who is responsible? The manufacturer, the AI developer, or the owner?
- Ethical Decisions: Autonomous vehicles may face situations where they need to make moral decisions, such as deciding how to respond to an unavoidable collision. How these ethical dilemmas are handled is a critical issue for the industry.
Section 4: Future of AI in Autonomous Driving
4.1 AI Integration with Other Technologies
As autonomous driving technology matures, we can expect AI to integrate with other emerging technologies:
- 5G Connectivity: The introduction of 5G networks will provide faster data transmission, enabling real-time communication between autonomous vehicles and infrastructure (e.g., traffic signals, road sensors).
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): V2X communication allows vehicles to interact with each other and the surrounding infrastructure, improving safety and coordination.
4.2 Full Autonomy and Urban Mobility
The ultimate goal of autonomous driving technology is to achieve full autonomy (Level 5). As AI continues to advance, we can expect to see fully autonomous vehicles that can navigate any environment without human intervention. This could pave the way for new urban mobility solutions, such as autonomous ride-sharing services, which may transform how we think about transportation.
Section 5: Case Studies of Successful AI Implementation in Autonomous Vehicles
5.1 Tesla Autopilot
Tesla’s Autopilot system is one of the most well-known AI-driven autonomous driving technologies. Through continuous software updates and real-world driving data, Tesla vehicles have been able to improve their autonomous capabilities. Autopilot’s use of AI enables Tesla cars to perform tasks such as highway driving, parking, and collision avoidance, moving closer to fully autonomous driving.
5.2 Waymo’s Autonomous Taxi Service
Waymo has achieved significant milestones in autonomous driving, with its fleet of fully autonomous vehicles providing public taxi services in Phoenix, Arizona. Waymo’s vehicles rely on AI-powered sensors, cameras, and mapping technologies to navigate safely through complex urban environments.
5.3 Cruise by General Motors
Cruise, an autonomous driving division of General Motors, has been developing self-driving technology with the goal of launching a commercial autonomous taxi service. Cruise’s vehicles use AI, machine learning, and computer vision to navigate streets without human intervention, with a focus on providing safe, efficient transportation.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is the driving force behind the development of autonomous driving technology. Through the use of machine learning, computer vision, sensor fusion, and other AI techniques, autonomous vehicles are becoming more capable of navigating and interacting with their environments. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, Audi, and General Motors are leading the way, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in self-driving technology.
However, there are still significant challenges to overcome, including data quality, safety testing, and legal considerations. As AI continues to evolve and integrate with other emerging technologies, the future of autonomous vehicles looks increasingly promising. With ongoing advancements, we are moving closer to the realization of fully autonomous transportation, which could fundamentally change how we travel and interact with the world around us.











































